Global ammonia demand is projected to reach approx. 204 million metric tons in 2025, reflecting a steady year-on-year increase. This increase reflects a steady upward trend driven by strong demand across multiple sectors most notably in agriculture, where ammonia serves as a critical building block for nitrogen-based fertilisers. Urea, the most prominent ammonia derivative, is expected to set a new production record in 2025, fuelled by continued growth in global food demand and efforts to enhance crop yields.
Beyond fertilisers, ammonia also plays a key role in the production of ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulphate, nitric acid, and various industrial chemicals. With rising momentum behind global decarbonisation, ammonia is being increasingly recognised for its potential role as a hydrogen transport medium and emissions-free energy source, especially in marine and energy sectors. This emerging demand is expected to contribute to long-term capacity expansion and new investment in low-carbon (green and blue) ammonia technologies.
- North America, Central & East Asia, and Eastern Europe are leading capacity additions.
- Decarbonised ammonia projects are a major area of investment, especially in North America.
- Consumption growth is projected at ~1-2 per cent annually, driven by fertiliser demand in Latin America, South Asia and other region.
Ammonia Price Analysis and Trend
Between January 2023 and June 2025, US ammonia prices experienced significant fluctuations, driven primarily by shifts in natural gas feedstock costs, agricultural demand cycles, and supply-side dynamics.
In 2023, ammonia prices declined sharply throughout the year, falling from $967/MT in January to around $554/MT in December a drop of over 40 per cent. This downward trend was closely tied to declining Henry Hub natural gas prices, which dropped from $161.24/MT in January to $124.21/MT by year-end. Ammonia production is highly sensitive to natural gas prices, as gas constitutes up to 85 per cent of production costs. Additionally, demand for ammonia weakened in the latter half of 2023 due to reduced fertiliser consumption amid erratic weather and delayed planting seasons in key agricultural regions. Oversupply conditions, both domestically and from global producers such as Russia and the Middle East, further pressured US prices.
From early to mid-2024, ammonia prices remained relatively subdued, with year-on-year declines ranging from 40 per cent to over 50 per cent in the first quarter. This was despite modest volatility in natural gas prices, suggesting that the ammonia market was still correcting from the high price levels seen in previous years. However, starting in mid-2024, ammonia prices began stabilising and gradually rebounding, as signs of improved agricultural demand emerged. Natural gas prices also began to rise again toward the end of 2024, influencing ammonia cost structures.
By early 2025, ammonia prices showed a marked recovery. January through March saw double-digit year-on-year growth, with March 2025 prices rising 39 per cent over March 2024 levels. This recovery can be attributed to several factors: a surge in natural gas prices (up by more than 40 per cent from December 2024 to February 2025), improved seasonal fertiliser demand ahead of the spring planting season, and possible supply tightening due to planned plant turnarounds or export pull from overseas markets. Between April and June 2025, ammonia prices continued their upward momentum, rising nearly 30 per cent year-on-year, indicating renewed market strength, tighter balances, and feedstock driven pricing pressures.
- April: $512/MT (2025) vs. $397/MT (2024) → +28.9 per cent
- May: $482/MT (2025) vs. $387/MT (2024) → +24.6 per cent
- June: $440/MT (2025) vs. $339/MT (2024) → +29.8 per cent
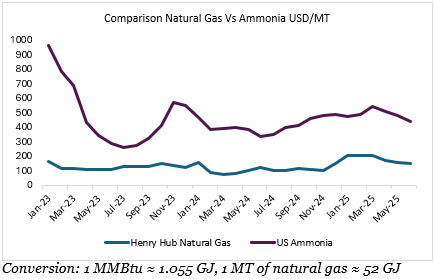
Overall, the period reflects the cyclical nature of the ammonia market, where feedstock prices and fertiliser demand play critical roles. The strong correlation observed between natural gas and ammonia prices in early 2025 suggests a return to cost-driven pricing, while the earlier decoupling in 2024 reflects residual oversupply and lagging demand from the agricultural sector.
Ammonia Pricing Snapshot (dollars/ton) July 2025
- North America FOB Caribbean: 407
- US FOB US Gulf: 445
- Asia FOB China: 323
- India Domestic Mumbai: 293
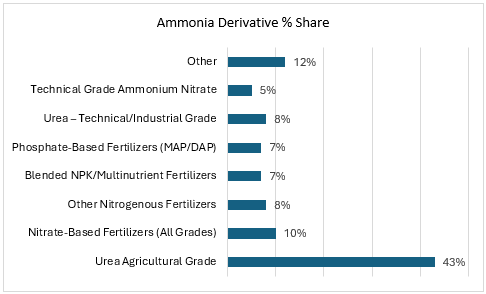
- 88 per cent used in fertilisers (urea, ammonium nitrates, ammonium phosphates, etc.)
- Also used in explosives, plastics, Fibers, and resins
KBR Awarded: KBR has been awarded a FEED contract by KEPPT for an ammonia and urea plant in Basra, Iraq. The project includes a 2,300 MTPD ammonia unit and a 3,850 MTPD urea facility using KBR’s proprietary technology. It aims to boost Iraq’s agricultural sector, reduce fertiliser imports, and create local employment. KBR brings global expertise, having supported over 260 ammonia plants worldwide.
BASF First Producer of Renewable Ammonia: BASF has become the first producer of renewable ammonia in Central Europe, marking a significant milestone in the decarbonisation of the regional ammonia value chain. The company has introduced two new sustainable product grades – Renewable Ammonia and Renewable Ammonia Solution 24.5 per cent – which are produced at its Ludwigshafen Verbund site.
This development is underpinned by the substitution of fossil-based hydrogen with hydrogen derived from renewable energy sources in BASF’s ammonia production process. The transition reduces the plant’s dependence on natural gas and aligns with broader goals to lower carbon emissions across the chemical industry.
Yara International Performance and Market Insight (1H 2025): From Yara's 2Q 2025 report:
- Ammonia Production (YTD): 3.46 million tons
- Ammonia Trade Deliveries (YTD): 0.93 million tons
- Some Low Carbon Ammonia Upcoming Capacities and many more…
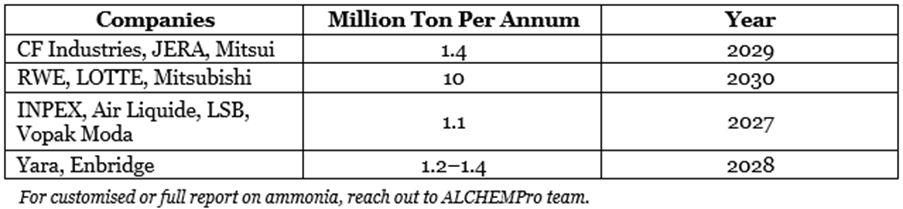
Yara is actively optimising its ammonia portfolio and investing in low-carbon ammonia projects in the US.
Strategic Implications and Trends
The ammonia market is transitioning from supply-driven to demand-driven dynamics. Long-term growth will be supported by global food demand and climate-resilient agriculture. Renewable ammonia is emerging as a future fuel and hydrogen carrier, drawing large investments.


