Sulphate of Potash (SOP), chemically known as Potassium Sulphate (K₂SO₄), is a high-value, chloride-free fertiliser widely recognised for its effectiveness in boosting crop yield and enhancing quality. Unlike conventional potash fertilisers, SOP contains no harmful chloride, making it the preferred choice for chloride-sensitive crops such as fruits, vegetables, tea, tobacco, and spices.
Rich in potassium (K) and Sulphur (S)—two essential nutrients for plant growth—SOP supports healthy root development, improves resistance to drought and disease, and enhances the colour, texture, and taste of harvested crops. It is particularly effective for intensive farming systems and modern irrigation setups.
- Free from Chlorides: Gentle on delicate crops and supports sustainable soil health over time
- Improves Plant Stress Tolerance: Enhances resistance to heat, drought, and disease
- Enhances Crop Quality: Improves visual appeal, taste, and post-harvest longevity
- Fully Water-Soluble: Well-suited for use in drip irrigation and fertigation applications
Market Overview
The global SOP market is witnessing steady growth, fuelled by rising food demand, expanding horticulture production, and a shift towards sustainable and organic farming practices. With increasing awareness of soil health and the drawbacks of chloride-based fertilisers, SOP is gaining traction worldwide.
- Estimated Market Value: Over $6 billion by 2025
- Projected Growth Rate: CAGR of 5.7 per cent by 2033
- Key Drivers: Soil degradation, precision farming, and high-value crop cultivation
- Asia-Pacific: Leading the demand surge, with strong adoption in India and China driven by high agricultural activity
- Europe & North America: Growing demand aligned with organic and sustainable farming trends
- Middle East & Africa: Adoption supported by SOP’s compatibility with saline soils and water-scarce regions
Production Landscape
There are two primary methods of SOP production:
- Mannheim Process: Reaction of Muriate of Potash (MOP) with Sulphuric acid
- Brine-Based Extraction: A natural, chemical-free route that extracts SOP from sea brine, offering lower production costs and a minimal environmental footprint
In India, ACIL stands as the only large-scale producer of fertiliser-grade, water-soluble SOP using the sea brine method. This eco-friendly process not only ensures high product purity but also supports the company’s commitment to sustainable agriculture. ACIL has also developed the capability to produce Schoenite, a potassium and magnesium-rich mineral used in multi-nutrient fertilisers.
- Price Analysis: Europe Export Market for Sulphate of Potash (SOP) and Muriate of Potash (MOP)
- Period Covered: January 2022 – March 2025
The European export pricing trends for Sulphate of Potash (SOP) and Muriate of Potash (MOP) reveal distinct market dynamics, driven by differences in product application, production methods, and supply-demand fundamentals.
SOP Pricing Trend (Potassium Sulphate)
Price Trend Summary: The price of SOP in Europe witnessed a steep surge from January 2022 to a peak in June 2022, climbing from approximately $760/MT to $1350/MT, marking a 77 per cent increase. This price rally was driven by global fertiliser supply disruptions due to the Russia-Ukraine conflict, compounded by energy price inflation and logistics constraints.
From this high, SOP prices gradually declined through 2023, bottoming out around $660/MT by August 2023, a 51 per cent decline from the peak. The price has since stabilised and remained relatively flat through to April 2025, hovering around $710/MT, representing a 47 per cent decrease from the 2022 peak.
Key Fluctuation Drivers
1. Geopolitical Tensions and Supply Disruption (Early 2022 – Mid 2022): The Russia-Ukraine war significantly disrupted potash exports from major producing nations such as Belarus and Russia, tightening MOP availability. As SOP production is partially dependent on MOP, supply bottlenecks led to cascading price hikes in both materials.
2. Energy Cost Surge and Inflation (2022): The energy-intensive Mannheim process experienced cost inflation due to natural gas and electricity price volatility in Europe.
3. Demand Contraction and Inventory Correction (2023): As global fertiliser buyers adjusted to elevated price levels, demand for premium fertilisers like SOP weakened, particularly in cost-sensitive markets. This led to inventory build-up and aggressive destocking, applying downward pressure on prices.
4. Stabilisation and Market Correction (2024–2025): From late 2023 onward, with energy markets stabilising and fertiliser trade routes normalising, SOP prices reached a steady-state. As of April 2025, SOP prices stand near $710/MT, still carrying a ~56 per cent premium over MOP (around $455/MT), reflective of its superior agronomic value and limited production routes.
MOP Price Influence: MOP prices followed a similar trajectory, rising from $520/MT in Jan 2022 to nearly $980/MT by July 2022 (an 88 per cent increase), before declining to $420/MT in mid-2023, and stabilising at $455/MT in April 2025. The cost volatility of MOP directly impacted SOP production costs, particularly where MOP is used as feedstock.
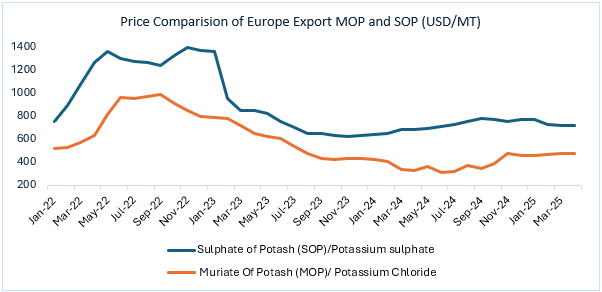
- Volatility Peak: Both products saw the highest volatility in 2022 due to global supply shocks.
- Price Correction: SOP experienced a sharper correction than MOP in early 2023.
- Market Stabilisation: Pricing began to stabilise by mid-to-late 2023, reflecting better market equilibrium.
Major Potash Producers by Country
- Nutrien Ltd. (Canada)
- The Mosaic Company (US)
- BHP Group Limited (Canada)
- Public Joint Stock Company Uralkali (Russia)
- Belaruskali (Belarus)
- Qinghai Salt Lake Potash Co., Ltd. (China)
- K+S Aktiengesellschaft (K+S AG) (Germany)
- DEUSA International GmbH (Germany)
- Israel Chemicals Ltd. (ICL) (Israel)
- Arab Potash Company PLC (Jordan)
- Lao Kaiyuan Mining Co., Ltd. (Laos)
- Sociedad Química y Minera de Chile S.A. (SQM) (Chile)
- Intrepid Potash, Inc. (US)


