Chemical Identity and Physical Properties
1,3-Butadiene is a colourless, highly flammable gas with a faint petroleum-like odour. Its molecular weight is approximately 54.1 g/mol. The substance boils near –4 °C (about 24 °F) and solidifies at roughly –109 °C (–164 °F). Although insoluble in water, it dissolves readily in alcohols and ethers. Because of its unsaturated molecular structure, butadiene can polymerise easily—particularly when oxygen is present so inhibitors and careful storage conditions are necessary to prevent unwanted reactions.
Feedstock and Production Process Overview
Most commercial butadiene is recovered as a co-product of ethylene and propylene steam cracking, where a C₄ hydrocarbon stream is separated from the cracker off-gas and processed through extractive distillation using solvents such as dimethylformamide (DMF) or N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP).
Steam Cracker By-Product Route
Contributes to more than 90 per cent of world output. Cracking heavier feeds such as naphtha yields larger quantities of C₄ components than lighter ethane feeds.
On-Purpose Routes
Growing adoption in regions with limited naphtha cracking capacity. Key examples include:
- Oxidative Dehydrogenation of n-Butane: Converts n-butane to butadiene via metal-oxide catalysts.
- Dehydrogenation of n-Butenes: Produces high-purity butadiene through catalytic conversion of mixed butenes.
- Ethanol-Based Routes: Applied mainly in coal- and biomass-rich economies (e.g., China) to derive butadiene from bio-ethanol via dehydration and dehydrogenation.
Application Spectrum and End-Use Industries
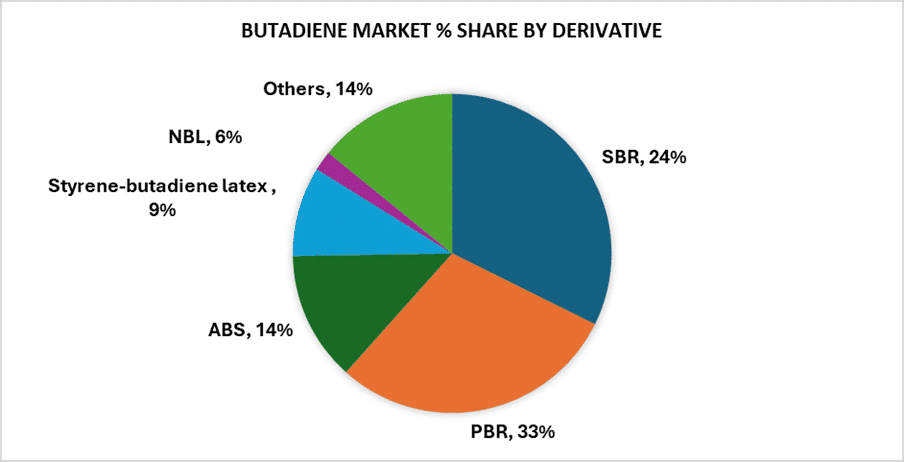
Butadiene is a cornerstone intermediate for the synthetic rubber and thermoplastic sectors. Roughly 60 per cent of global demand goes into the manufacture of polybutadiene (PBR) and styrene-butadiene (SBR) rubbers, both essential in tire, automotive, and mechanical-goods production.
Other major derivatives include acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) resins, styrene-butadiene latex, and adiponitrile, a precursor for nylon 6,6.
End-use applications range from tires, seals, hoses, and gaskets to carpets, coatings, adhesives, textiles, and engineering plastics.
Global 1,3-Butadiene Market Update (Week Ending October 2025)
Overview
Global 1,3-Butadiene (BD) prices reflected a mixed trend during the week ending October 2025, as regional fundamentals diverged across major markets. Softer feedstock naphtha values and weaker downstream synthetic rubber demand exerted downward pressure in Asia, while European and US markets remained broadly stable with balanced supply-demand dynamics.
United States
In the United States, 1,3-Butadiene prices were assessed at 29.5 cents per pound (CIF). Market fundamentals remained steady, supported by balanced inventory levels and consistent domestic offtake from styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) manufacturers. Lower upstream crude oil and naphtha values slightly eased cost pressure, but no major price corrections were observed due to stable demand from tire and automotive sectors.
Europe
In Northwest Europe, FD prices stood at EUR 710 per ton, while FOB Rotterdam prices were reported at $630 per ton. European BD values held relatively firm as steady cracker operations ensured adequate supply, though overall downstream consumption remained moderate. Market participants noted limited export opportunities amid weak Asian arbitrage and subdued automotive demand, which capped any potential price gains.
Asia-Pacific
Asian markets demonstrated a softer tone across key subregions, driven by a combination of sluggish downstream activity and oversupply in certain export-oriented economies.
- Northeast Asia: 1,3-Butadiene prices were assessed at $960 per ton (CFR). Market sentiment was largely flat, with weak spot demand counterbalanced by stable operating rates at integrated complexes.
- China: CFR China prices declined to $950 per ton, reflecting muted buying interest from domestic rubber manufacturers and elevated stock levels.
- South Korea: FOB South Korea prices declined to $920 per ton, weighed down by limited export activity amid subdued industrial demand and weakened buying confidence stemming from geopolitical uncertainties.
- Southeast Asia: CFR Southeast Asia prices were around $860 per ton, indicating weak demand and minimal import activity across the region.
Production Technologies
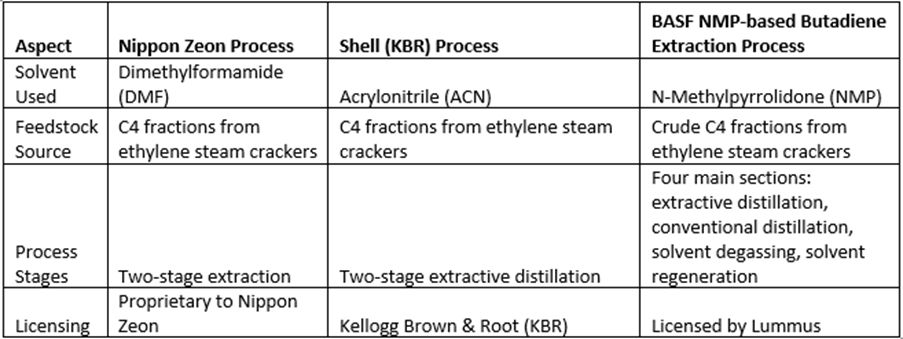
The Nippon Zeon process is a two-stage method that utilises dimethylformamide (DMF) as the solvent. The primary feedstock for this process typically consists of the C4 fraction obtained from ethylene steam cracking, making it effective for extracting butadiene.
In contrast, the Shell process operates similarly to both the Nippon Zeon and BASF processes, with the main distinction being its use of acrylonitrile (ACN) as the solvent. This process is licensed by Kellogg Brown & Root (KBR) and is designed to optimise the extraction of butadiene from C4 streams.
Market Drivers
The global BD market during the week was influenced by multiple interlinked factors:
- Feedstock trends: Softer naphtha and crude oil benchmarks reduced overall production costs, particularly in Asia.
- Downstream demand: Marginal slowdown in SBR, PBR, and ABS production curtailed spot Butadiene consumption.
- Trade dynamics: Limited arbitrage between Asia and Europe constrained price movement, while steady US consumption balanced the overall global outlook.

-b2_Big.jpg)
