Adipic Acid, a critical chemical primarily used in Nylon-6,6, polyurethanes, plasticisers, and resin systems, faced a generally weak pricing environment across global markets during 2024–2025. Prices declined due to a combination of expanding Asian production, sluggish downstream polymer demand, and softer raw material costs, particularly benzene and cyclohexane. Because adipic acid is a globally traded commodity, its pricing trends also provide insights into engineering plastics, automotive demand cycles, and intermediate chemical markets.
Global Supply Structure
China and South Korea remain the largest producers worldwide, exerting significant influence on regional pricing:
- China accounts for a substantial portion of global capacity, giving it the ability to influence global price floors.
- South Korea focuses on high-purity grades and maintains export-oriented supply chains.
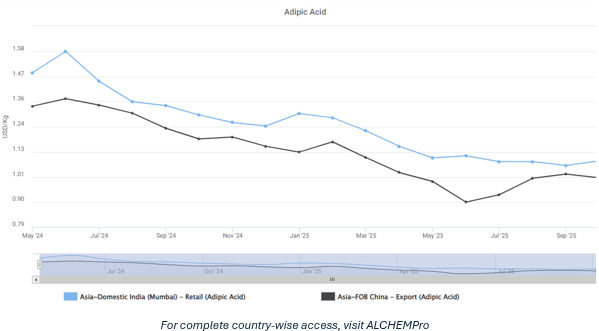
Adipic Acid Price Trend (2024–2025)
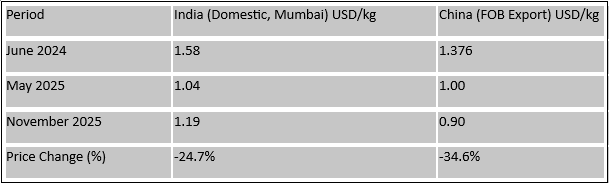
1. China’s sharper decline reflects high production rates, structural oversupply, aggressive export strategies, and weak domestic consumption in Nylon-6,6.
2. India experienced a more moderate drop due to import-linked pricing, shipping and margin adjustments, currency effects, and recently stronger domestic demand coupled with tighter distributor inventories.
3. The price difference between India and China, averaging around 180–250 dollars/ton, continues to be influenced by logistics, duties, and local markups
Upstream Cost Dynamics
The economics of adipic acid production are strongly linked to benzene, cyclohexane, and KA Oil (a mixture of cyclohexanone and cyclohexanol), along with nitric acid and energy costs:
- Benzene: Global prices declined significantly during 2024–2025, easing cost pressures on adipic acid producers.
- Cyclohexane: Oversupply in Asia and higher refinery output kept prices low. Integrated Chinese producers gained cost advantages through benzene-to-cyclohexane conversion.
- Nitric Acid: Remained stable globally, with no significant disruptions affecting conversion costs.
- Energy Costs: European producers faced high electricity and gas prices, while Asian integrated facilities, particularly in China, benefited from lower energy costs.
These factors collectively supported the downward pricing trend observed across Asia.
Downstream Consumption Dynamics
Adipic acid demand is primarily driven by Nylon-6,6 (around 55 per cent of global usage) and polyurethanes:
- Nylon-6,6: Weak automotive production, especially in Europe, and reduced consumption in electrical, electronic, and industrial plastics contributed to muted demand.
- Polyurethanes: Demand remained stable but did not offset weakness in Nylon-6,6 markets.
Regional Price Differentiation and Trade Behaviour
- China: With roughly half of global capacity and high operating rates, Chinese export prices effectively set the floor for South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Middle Eastern procurement benchmarks.
- Western Markets (EU and US): Prices were higher due to energy costs and environmental compliance requirements, such as nitrous oxide abatement.
Europe Flags Significant Dumping Margins on Chinese Adipic Acid Imports
The Union’s ongoing trade investigation has identified significant provisional dumping margins on adipic acid imports from China, with rates ranging from 28.6 per cent to 46.8 per cent, underscoring notable under-pricing in the regional market. These findings may influence sourcing strategies and cost structures for downstream users in polyurethane systems, Nylon-6,6, adhesives, plasticisers, and specialty materials. A final determination is expected in early 2026, which will play a pivotal role in shaping future market dynamics and pricing behaviour across the adipic acid value chain.

-b_Big.jpg)
