Ammonium nitrate and its primary derivative, Ammonium Nitrate Fuel Oil (ANFO), are widely applied as high-efficiency nitrogen fertilisers and as key oxidising agents in commercial explosives used for mining, quarrying, and infrastructure development. These applications support major end-use industries such as agriculture, mining, construction, and civil engineering, where ammonium nitrate enables crop nutrition, controlled blasting, rock fragmentation, and drilling operations for resource extraction and large-scale project execution.
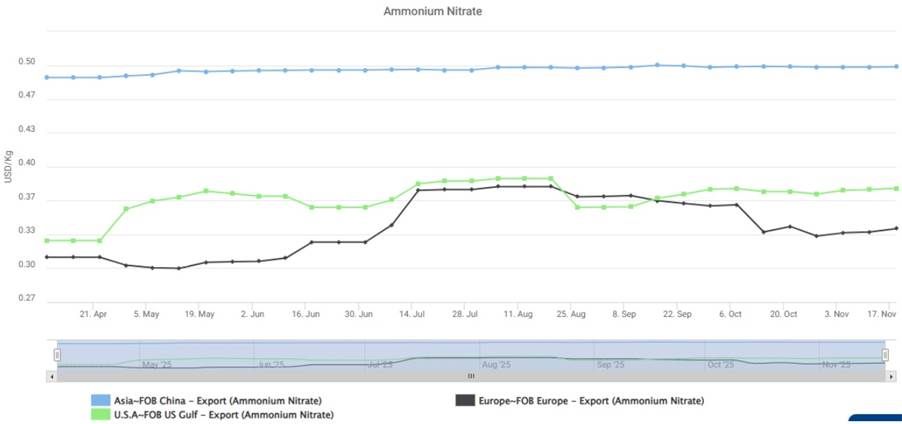
Ammonium nitrate (AN) pricing exhibited clear regional divergence between April and November 2025, driven primarily by feedstock cost variability, differing supply demand balances, and localised logistics dynamics:
- Asia (FOB China) maintained a narrow, steady band near $0.49–0.50/kg, highlighting a stable supply environment supported by consistent production and low volatility in input cost.
- Europe (FOB Europe) demonstrated the most pronounced intraregional volatility, climbing from 0.30/kg to 0.37/kg by mid-summer before moderating toward 0.34–0.36/kg in Q4.
- US Gulf (FOB US Gulf) exhibited mid-range volatility, rising from 0.30/kg in April to 0.38/kg in July, followed by a decline into the 0.32–0.33/kg range before modest recovery.
Asia (FOB China)
Price Range: 0.49–0.50/kg
Trend: Stable
- China’s price flat structure, signalling a well-balanced market with minimal supply disruptions.
- Chinese production capacity remained adequate for both domestic and export commitments, and the region showed limited sensitivity to global feedstock price swings during the period.
- The stability suggests effective hedging or strong supply chain resilience in the upstream ammonia and nitric acid segments.
Conclusion: China with stability reflecting consistent operating rates and stable demand.
Europe (FOB Europe)
Price Reference: 0.30-0.37/kg
Trend: Prices rose in early months, stabilised through mid-year, and then softened gradually toward the year’s end.
Europe displayed the highest price sensitivity, consistent with well-known structural factors:
1. Feedstock Exposure:
European ammonia production remains exposed to natural gas pricing volatility. The early-summer rise aligns with seasonal tightening in gas markets.
2. Operational Constraints:
Maintenance cycles in Ammonium Nitrate plants often occur in mid-year, reducing output and temporarily tightening supply.
3. Demand Pulses:
Agricultural purchasing cycles (pre-harvest and winter fertiliser preparation) typically create demand surges that amplify price rises when supply is constrained.
4. Logistics Tightness:
Port and freight costs occasionally firm during summer.
Conclusion: Europe’s fluctuating curve represents a classic case of cost-push and seasonal-pull dynamics.
United States (FOB US Gulf)
Price Range: 0.30-0.36/kg
Trend:
- Starting near 0.30–0.31/kg in April
- Rising to 0.36/kg mid-July
- Easing back to 0.32-0.33/kg by November
The US Gulf prices followed a moderate volatility cycle, driven by:
- Ammonia Input Costs: US natural gas prices remained comparatively stable, but temporary spikes in Q2 pushed ammonium nitrate costs upward into the July peak.
- Industrial Demand Swings: Mining and construction explosives demand influenced the mid-year upward pressure.
- Logistical Impacts: Seasonal weather patterns created temporary freight and supply-chain disruptions, reflected in short-term peaks.
Conclusion: The US market displayed an intermediate volatility profile more stable than Europe but more reactive than Asia reflecting diversified demand and resilient feedstock availability.
Key Insights
China’s pricing reflects cost stability, not necessarily low cost; its export- ammonium nitrate is priced higher but moves in a tight band.
Europe is cost-sensitive, creating the broadest price range.
The US behaves as balancing domestic industrial demand with relatively steady feedstock economics.
Technical Drivers Behind the Observed Price Movements
Upstream Influence
Ammonia remains the primary cost driver. Variability in natural gas markets especially in Europe translates into proportional Ammonium nitrate price movement.
Supply-Side Constraints
Temporary reductions in nitric acid or Ammonium nitrate production capacity (planned maintenance, weather disruptions) correlate with mid-year price elevations, especially visible in Europe and the US
Demand-Side Patterns
Agriculture (Europe) and mining/construction (US) generated distinct, region-specific demand pulses that shaped the peaks.
Market Structure
- China’s price suggests strong inventory management and high production continuity.
- Europe’s reactive curve signals tight structural balance any disturbance creates tangible price impact.
- The US shows mixed influence, reacting to both domestic factors and global trade flows.
Outlook and Strategic Considerations
Short-Term Outlook (Q4 2025 – Q1 2026)
- Asia likely remains stable
- Europe may experience renewed volatility if winter gas prices fluctuate.
- US expected to stay range-bound with potential slight upside if industrial demand strengthens.


