Sulphur markets in Asia have entered a period of noticeable tightening. Port quotations have been climbing steadily and are now approaching levels last seen during earlier peaks. The current situation is being shaped by a mix of global and regional factors: lower international production, reduced cargo arrivals at key Asian ports, and more proactive raw-material procurement by downstream industries. These developments are also reflected in the evolving import profiles of major consumers such as Indonesia, China, India and others.
India Sulphur Powder Market: Price Momentum and Technical Trend
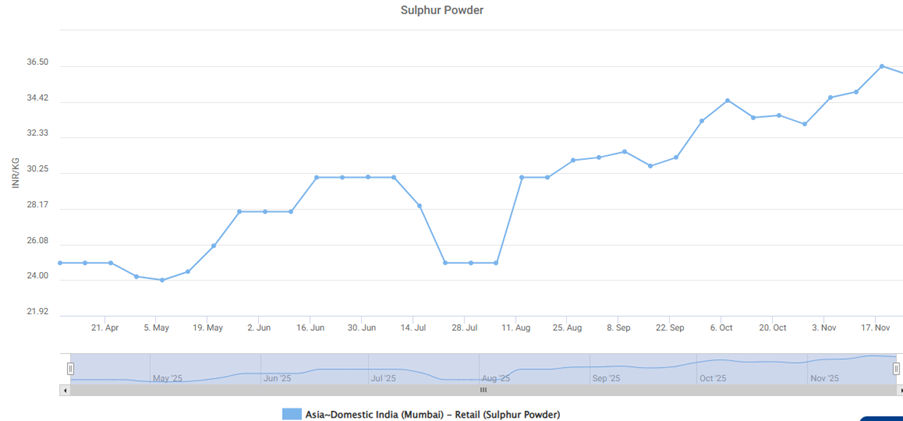
In India, sulphur powder prices have continued their upward momentum throughout the year. Values have advanced from roughly ₹24/kg in late April to around ₹37/kg by mid-November—representing an increase of about 54 per cent over seven months.
The price escalation is tied to several structural pressures within the sulphur supply chain:
- Port receipts have been limited, while global spot availability remains constrained, tightening access to raw sulphur.
- Inputs used for manufacturing sulphur-based intermediates, especially sulphuric acid, have become more expensive, adding to production costs.
- Fertiliser producers particularly within the phosphate segment have sustained consistent procurement activity, while several non-fertiliser downstream industries are exhibiting softer demand due to subdued consumption trends in their end-use markets.
Taken together, these elements place the Indian sulphur market in line with broader regional dynamics: a backdrop of firm demand, elevated input costs, and little near-term relief on the supply side. This combination points toward a relatively strong price environment as the next quarter approaches.
Indonesia: Strong Dependence on Middle Eastern Suppliers
Indonesia’s dependence on Middle Eastern-origin sulphur remains pronounced. Most of its import volumes are sourced from Gulf producers, with only modest supplementary shipments coming from Taiwan, Singapore, and a few other locations.
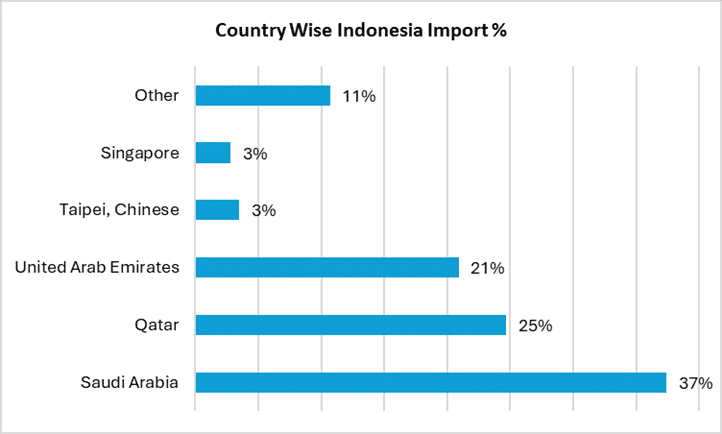
This concentration means that any disruption or adjustment to Gulf export availability can translate rapidly into shifts in Indonesian procurement activity, especially for fertiliser and industrial acid producers.
China: Broad and Balanced Sourcing Strategy
China maintains a far more diversified import strategy. Its sulphur inflows are split across several major producing regions, allowing it to adjust more easily when global availability fluctuates.
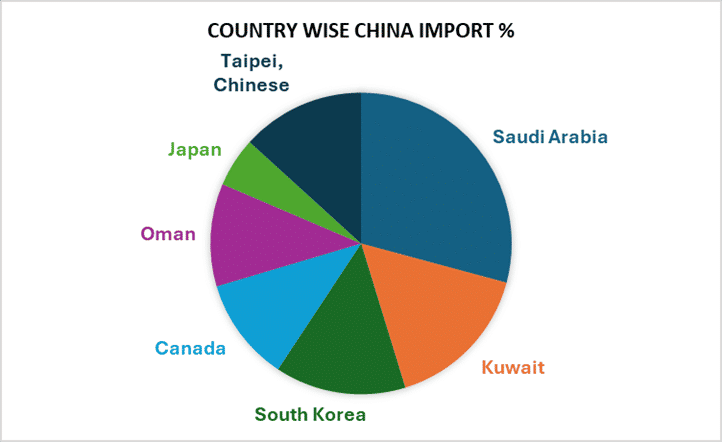
While this diversity gives China some insulation from price shocks, domestic sulphuric-acid manufacturers are still facing increasing raw-material costs due to global tightness.
India: Highly Concentrated Import Pattern
India’s sulphur procurement remains heavily concentrated in the Gulf:
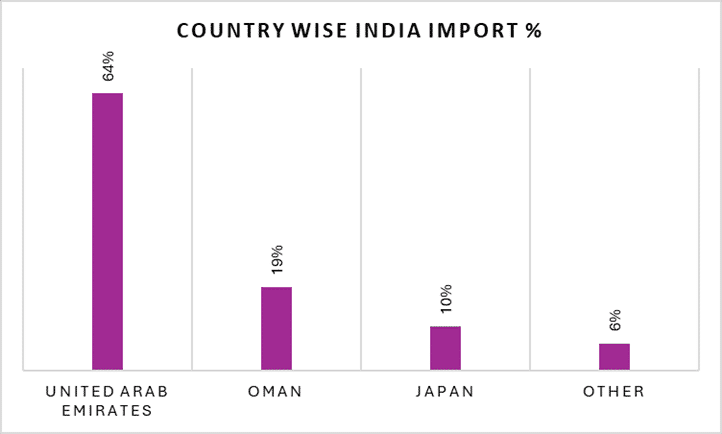
India continues to source most of its sulphur requirements from Gulf suppliers. This narrow import base means that Indian buyers tend to be more sensitive to Middle Eastern production trends and pricing movements. The impact becomes even more pronounced during periods of limited global supply, such as the current environment.

-b_Big.jpg)
