Lithium Carbonate has emerged as one of the most strategically important battery materials, underpinning the rapid growth of electric vehicles (EVs), energy storage systems (ESS), and portable electronics. As global decarbonisation accelerates, lithium carbonate demand has strengthened across major economies, driving price volatility and reshaping upstream and downstream supply chains. This article examines the lithium carbonate value chain, recent price movements, and regional market dynamics, with particular focus on China, Chile, Argentina, and the United States.
Lithium Carbonate Value Chain
The lithium carbonate market operates through a vertically linked value chain comprising resource extraction, refining and conversion, and downstream battery and industrial applications.
Upstream: Lithium Extraction and Processing
1. Brine-Based Extraction
Lithium-rich brines are pumped from underground reservoirs into evaporation ponds, where solar evaporation concentrates lithium salts. These concentrates are chemically processed to produce lithium carbonate. Brine extraction offers lower operating costs but involves longer processing cycles, making output less flexible during demand surges.
Chile and Argentina dominate this segment due to high-grade brine resources and favourable climatic conditions.
2. Hard Rock (Spodumene) Mining
Spodumene ore is mined, crushed, and beneficiated to produce lithium concentrate. The concentrate is then transported to chemical plants for conversion into lithium carbonate. While more energy-intensive than brine extraction, hard rock mining allows faster production ramp-up, supporting short-term supply responsiveness.
Australia is the primary source of spodumene feedstock, much of which is processed in China.
3. Emerging Extraction Technologies
Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE) technologies are being developed to shorten production timelines, improve recovery rates, and reduce environmental impact. Although still at early commercialisation stages, DLE could significantly alter future lithium supply economics, particularly in South America and North America.
4. Midstream: Refining and Conversion
Refining is a critical stage where raw lithium materials are converted into battery-grade lithium carbonate.
Key refining steps include:
- Removal of impurities such as magnesium, calcium, and boron
- Chemical conversion using soda ash or acid-based processes
- Crystallisation and drying to meet battery-grade purity standards
China leads global refining capacity due to its advanced chemical processing infrastructure and proximity to battery manufacturers.
Price Dynamics: Recent Surge Driven by EV and Energy Storage Demand
The Lithium Carbonate prices highlight a strong upward price movement from early December 2025 to early January 2026, reflecting tightening supply and strengthening downstream demand.
At the start of December 2025, lithium carbonate prices were approximately $11,500 per metric ton. Prices rose steadily through mid-December, supported by improving procurement activity from battery material producers. The upward momentum accelerated in the latter half of the month as EV battery output increased, and year end restocking activity intensified.
By early January 2026, prices reached around $16,700 per metric ton, translating into an approximate 45 per cent increase from the first week of December.
Additional Market Support Factors
- Producers Increasing Output: Lithium producers have started increasing production as demand supply fundamentals improved and order visibility strengthened.
- Inventory Reduction: Declining lithium carbonate inventories across the supply chain reduced spot availability, amplifying price momentum.
- Healthier Demand Supply Balance: Improved consumption from EV and energy storage sectors encouraged producers to operate at higher utilisation rates.
The sustained upward trend underscores lithium carbonate’s sensitivity to downstream battery demand and highlights strong structural support.
Lithium Carbonate Market Scenarios–2026
Strong growth in electric vehicle production and continued expansion of energy storage systems drive steady demand for lithium carbonate. Incremental supply from Argentina, Australia, and China partially offsets demand growth, but ramp-up limitations keep the market moderately tight. Inventory levels remain below historical averages, supporting prices in the $22,500–24,500 per metric ton range, with reduced volatility due to improving refining utilisation and long-term offtake agreements.
Tight Supply Environment
EV adoption and energy storage deployments exceed expectations, while supply ramp-ups face operational delays. Low inventories persist, amplifying lithium carbonate’s high price elasticity. Under this scenario, battery-grade prices could rise to $24,800–27,000 per metric ton, particularly during peak seasonal demand periods.
Supply Normalisation
Faster-than-expected capacity ramp-ups in South America and China, combined with inventory rebuilding and efficiency gains in battery chemistries, ease market tightness. Long-term contracts dominate spot transactions, reducing price volatility. Prices stabilise or soften to the $19,500–22,000 per metric ton range.
Downstream: Battery and End-Use Applications
Electric Vehicles
Lithium carbonate is a key input for lithium-based battery and other lithium-based chemistries used in EV batteries. Growing EV penetration across China, Europe, the US, and emerging markets continues to anchor long-term demand growth.
Energy Storage Systems
Energy storage has become one of the fastest growing lithium carbonate demand segments. Utility-scale renewable integration, grid balancing, and backup power systems are driving significant capacity additions.
Regional Market Dynamics–Lithium Carbonate
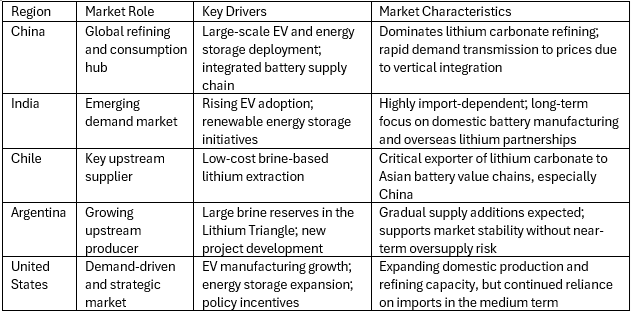
Major Lithium Carbonate Producers
Leading global lithium carbonate manufacturers include:
- Albemarle
- SQM
- Pilbara Minerals
- Lithium Americas
- Livent
- Tianqi Lithium
- Ganfeng Lithium

-b_Big.jpg)
