
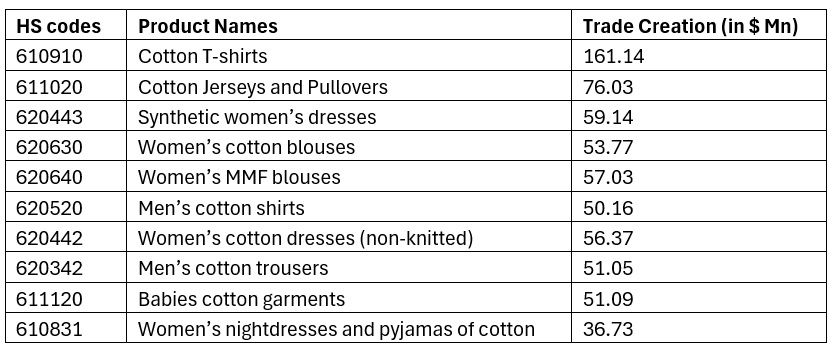
Table 1: India’s top 10 apparel products set to benefit from the India-EU FTA (in $ Mn)
Source: Analysis using the SMART tool
Trade Creation Effect
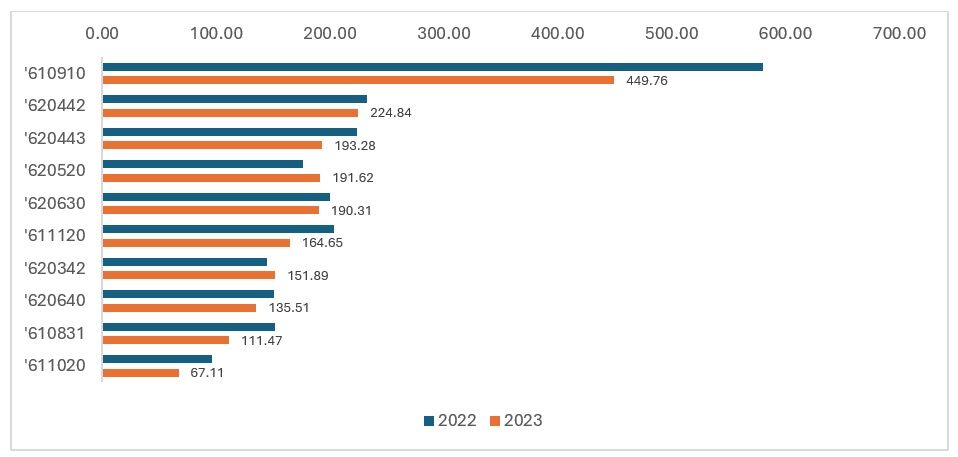
According to the SMART simulation, predominately, cotton products and particularly women’s products are set to gain from the lowered tariffs. Cotton T-shirts reign supreme, and India can be a global leader in the category. The list is dominated by cotton products of all types—T-shirts, blouses and trousers. However, India’s sunrise sectors such as synthetic women’s dresses and man-made fibre-based women’s blouses will get the required attention from the government if allowed to expand in key international markets such as the EU. A category to which India’s apparel exporters have given a lot of attention is the baby apparel segment, particularly cotton-based baby garments. India could beat several leading apparel exporting countries, given the general preference for cotton-based baby garments, owing to their softness and breathability. However, Indian baby apparel exporters need to follow the strict REACH 16 regulation and European Standard EN 14682 to be the dominant player in the EU.
Exhibit 1: India’s exports of top 10 apparel in CY 2022 and CY 2023 (in $ Mn)
Source: ITC TradeMap, F2F Analysis
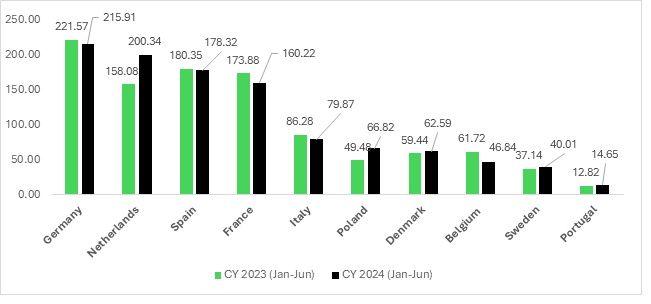
India’s performance in the top 10 EU countries during CY 2024 (January-June) has shown notable growth in select markets such as Denmark, Sweden, and Portugal. Among the top five EU economies, the Netherlands stands out as the only country where India’s selected products have performed better in CY 2024 (January-June) compared to CY 2023 (January-June). While India has effectively penetrated emerging economies within the EU, its declining performance in major EU economies in 2024 is a cause for concern.
Exhibit 2: India’s exports to key EU economies in CY 2023 (Jan-Jun) and CY 2024 (Jan-Jun) (in $ Mn)
India's Apparel Export Performance in Top European Markets: CY 2023 vs CY 2024 (January-June)
The data highlights a shifting dynamic in India’s apparel exports to its key European markets during CY 2024 (January-June) compared to the same period in CY 2023. While some countries demonstrate promising growth, others reflect slowing trends or declines, indicating varied challenges and opportunities across the region.
Key Highlights
Overall Analysis
India’s apparel exports to Europe reveal mixed patterns of performance in CY 2024 (January-June). While markets like the Netherlands and Poland show robust growth, significant declines in key economies like France, Germany, and Italy highlight emerging challenges. The sharp drop in Belgium further adds to concerns, though steady growth in Denmark, Sweden, and Portugal provides some balance.
This data underscores the need for India to re-evaluate its strategies for the EU market, focusing on sustaining growth in emerging economies and addressing stagnation or decline in major markets.
Welfare Effect on EU Consumers
The following gives an idea of the welfare effect on EU consumers if the India-EU agreement is signed. The motive for any trade agreement is to benefit the consumers on both sides of the agreement.
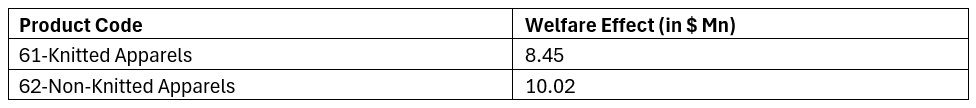
Table 2: Welfare effects for the EU consumers (in $ Mn)
Source: Analysis using the SMART tool
EU consumers are set to gain from the agreement, especially for non-knitted Indian apparel. EU consumers are set to benefit from a higher number of choices in both categories. The total welfare effect for EU consumers is projected at $18.47 million, which means that products worth $18.47 million have the potential to be imported into the EU.
Road Ahead
India’s cotton apparel sector is poised to benefit significantly from the India-EU trade agreement, but this opportunity comes with its own set of challenges and considerations. India has a vertically integrated cotton industry, allowing it to efficiently produce and process cotton, but this system is also vulnerable to fluctuations in cotton prices, which are often driven by unpredictable weather conditions. While the trade agreement could stimulate increased cotton apparel production, boosting India’s apparel exports, it could also lead to challenges in sourcing cotton due to rising prices.
Bangladesh, a key importer of Indian cotton for its finished apparel industry, is currently grappling with a crisis, potentially leading to a reduction in demand for Indian cotton. This could prompt Indian cotton manufacturers to focus more on the domestic market, which could benefit Indian apparel manufacturers by ensuring a steady supply of cotton for local production.
India’s strength lies in its production of women’s apparel and baby garments, both of which have strong export potential. To maximise returns, Indian apparel exporters should focus on these sub-categories, which offer high growth opportunities in international markets. By strategically targeting these sectors, India can capitalise on the trade agreement and further solidify its position in the global apparel market.
ALCHEMPro News Desk (NS)
Receive daily prices and market insights straight to your inbox. Subscribe to AlchemPro Weekly!