
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s GST reforms, anchored in dual rates of 18 per cent and 5 per cent with a narrow 40 per cent band for de-merit goods, have simplified taxation for the chemical sector. The restructuring has eased input levies on fertilisers, acids, and intermediates, corrected duty distortions, and enhanced cost efficiency. These measures are expected to strengthen supply-chain stability, boost domestic competitiveness, and reinforce India’s global chemical footprint. Additionally, broader structural reforms will streamline compliance, refund processing, and classification clarity, which are vital for Indian chemical manufacturers — especially those dealing with diverse product lines and export-import complexity.
Chemical Sector GST Impact Matrix – Next-Generation Reforms (2025)
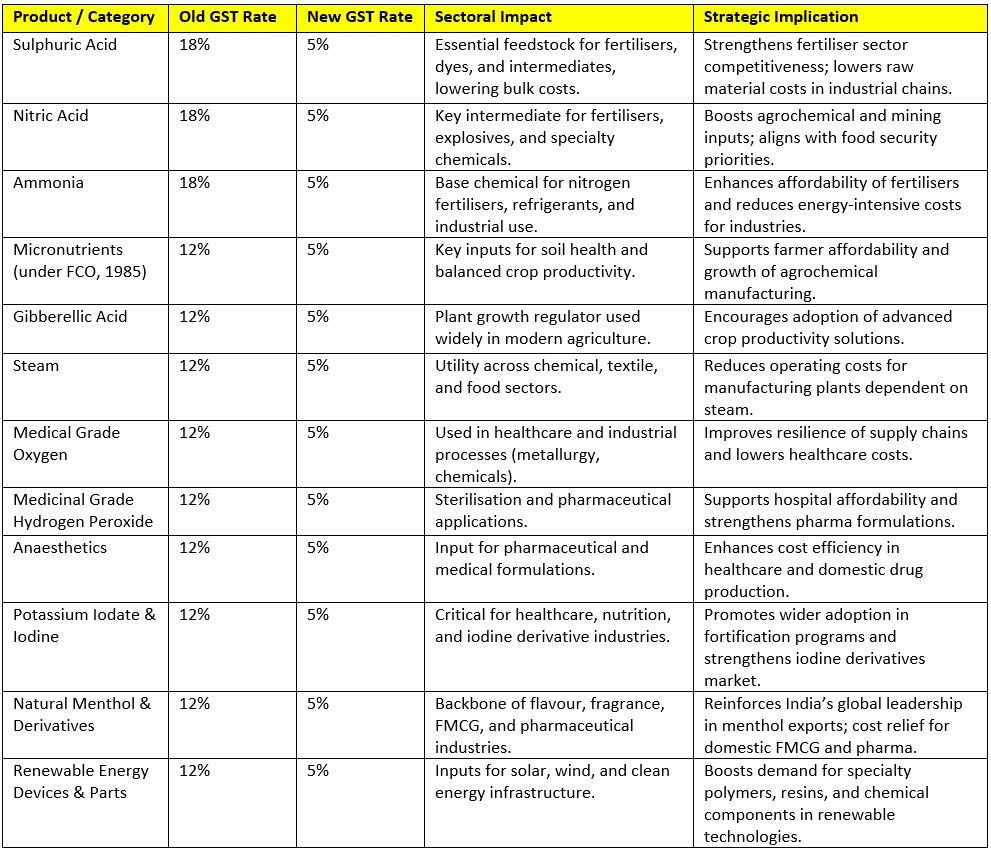
Domestic Market Impact
Export Market Impact
Why Now? Is There a Link to Trump-Era Tariffs?
Although Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman clarified that the recent GST overhaul wasn’t directly prompted by international tariffs, its timing and structure indicate a broader strategic intent:
1. Countering Trade Pressures by Stimulating Domestic Demand
With USduties on Indian exports reaching nearly 50 per cent in some cases, India appears to be shifting focus toward strengthening its domestic market to maintain economic momentum.
2. Building Economic Resilience in a Volatile Global Landscape
The GST 2.0 reforms are seen by many analysts as a timely move to reduce reliance on exports by encouraging internal consumption—particularly ahead of the crucial festive season.
3. Supporting MSMEs and Export-Sensitive Industries
The reduced tax burden on sectors like textiles, food processing, and light manufacturing provides relief to industries that are most exposed to foreign tariff pressures.
4. Boosting Business Confidence
Streamlining tax procedures, expediting refund mechanisms, and reducing rates are all measures aimed at strengthening investor sentiment—especially important during periods of global trade instability.
Conclusion
India’s recent GST reforms primarily aim to simplify the tax structure, make essential goods more affordable, and stimulate economic growth. At the same time, they represent a strategic effort to strengthen the domestic economy against global uncertainties—particularly those arising from protectionist measures like Trump-era tariffs. By boosting internal consumption and streamlining compliance, these changes are intended to cushion the economy from external trade shocks and maintain fiscal stability.
ALCHEMPro News Desk (VK)
Receive daily prices and market insights straight to your inbox. Subscribe to AlchemPro Weekly!